Can a Paternity Test Distinguish Between Father and Son
DNA paternity testing is the utilise of Dna profiles to make up one's mind whether an individual is the biological parent of another individual. Paternity testing tin be especially important when the rights and duties of the father are in outcome and a child's paternity is in dubiety. Tests tin as well determine the likelihood of someone beingness a biological grandparent. Though genetic testing is the nigh reliable standard, older methods also exist, including ABO blood grouping typing, analysis of diverse other proteins and enzymes, or using human leukocyte antigen antigens. The current techniques for paternity testing are using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). Paternity testing tin at present besides be performed while the woman is still pregnant from a blood draw.[1] [ii]
Deoxyribonucleic acid testing is currently the most advanced and accurate technology to determine parentage. In a Deoxyribonucleic acid paternity test, the result (chosen the 'probability of parentage)[3] [ failed verification ] is 0% when the declared parent is non biologically related to the child, and the probability of parentage is typically 99.99% when the declared parent is biologically related to the child. However, while almost all individuals accept a single and distinct set up of genes, rare individuals, known as "chimeras", have at least two different sets of genes, which tin outcome in a false negative result if their reproductive tissue has a different genetic make-up from the tissue sampled for the examination.[4]
Paternity or maternity testing for child or adult [edit]
The DNA test is performed by collecting buccal (cheek) cells found on the inside of a person's cheek using a buccal or cheek swab. These swabs have wooden or plastic stick handles with a cotton on synthetic tip. The collector rubs the inside of a person'due south cheek to collect as many buccal cells every bit possible, which are and then sent to a laboratory for testing. Samples from the alleged male parent or female parent and the child would exist needed.
Prenatal paternity testing for unborn child [edit]
Invasive prenatal paternity testing [edit]
It is possible to determine who the biological father of the fetus is while the woman is still pregnant through procedures called chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis. Chorionic villus sampling retrieves placental tissue in either a transcervical or transabdominal mode. Amniocentesis retrieves amniotic fluid by inserting a needle through the pregnant female parent's abdominal wall. These procedures are highly accurate because they are taking a sample directly from the fetus; however, there is a pocket-sized take a chance for the woman to miscarry and lose the pregnancy equally a upshot. Both CVS and Amnio crave the significant adult female to visit a genetic specialist known as a maternal fetal medicine specialist who will perform the procedure.
Not-invasive prenatal paternity testing [edit]
Advances in genetic testing have led to the ability to place the biological father while the adult female is nonetheless pregnant. At that place is a small amount of fetal DNA (cffDNA) nowadays in the mother's blood during pregnancy. This allows for accurate fetal Dna paternity testing during pregnancy from a blood draw with no risk of miscarriage. Studies accept shown that cffDNA tin offset exist observed equally early as vii weeks gestation, and the amount of cffDNA increases as the pregnancy progresses.[five] [6]
DNA profiling [edit]
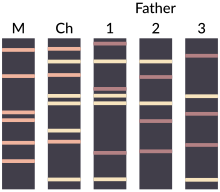
Example of DNA profiling in order to determine the father of a child (Ch). Child'south DNA sample should contain a mixture of different size DNA bands of both parents. In this case person #ane is likely the father
The Deoxyribonucleic acid of an individual is the same in every somatic (nonreproductive) jail cell. Sexual reproduction brings the Deoxyribonucleic acid of both parents together to create a unique combination of genetic material in a new jail cell, so the genetic textile of an individual is derived from the genetic material of each parent in equal amounts; this genetic material is known as the nuclear genome of the individual, because it is plant in the nucleus.
Comparing the Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence of one person to that of another can prove if ane of them was derived from the other, only Deoxyribonucleic acid paternity tests are not currently 100% authentic. Specific sequences are examined to encounter if they were copied verbatim from i private'south genome; if so, then the genetic material of ane individual could have been derived from that of the other (i.e. i is the parent of the other). Besides nuclear DNA, mitochondria also accept their own genetic fabric called mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial DNA comes just from the mother, without whatever shuffling.
Proving a relationship based on comparing of the mitochondrial genome is much easier than that based on the nuclear genome. However, testing the mitochondrial genome tin can prove merely if ii individuals are related by common descent through maternal lines only from a mutual ancestor and is, thus, of limited value (i.eastward., information technology could not be used to exam for paternity).
In testing the paternity of a male child, comparing of the Y chromosome can be used, since it is passed directly from father to son.
In the U.s., the AABB has regulations for DNA paternity and family relationship testing, but AABB accreditation is not required. DNA exam results are legally admissible if the drove and the processing follows a chain of custody. Similarly in Canada, the SCC has regulations on Dna paternity and human relationship testing, merely this accreditation, while recommended, is not required.
The Paternity Testing Commission of the International Club for Forensic Genetics has taken up the job of establishing the biostatistical recommendations in accordance with the ISO/IEC 17025 standards.[7] Bio-statistical evaluations of paternity should be based on a likelihood ratio principle - yielding the Paternity Index, PI. The recommendations provide guidance on concepts of genetic hypotheses and calculation concerns needed to produce valid PIs, as well equally on specific issues related to population genetics.
History [edit]
The first course of any kind of parental testing was blood typing, or matching blood types between the child and alleged parent, which became bachelor in the 1920s, afterward scientists recognized that blood types, which had been discovered in the early 1900s, were genetically inherited. Under this class of testing, the claret types of the child and parents are compared, and it can be adamant whether there is whatsoever possibility of a parental link. For example, ii O blood type parents tin can produce a kid merely with an O blood type, and two parents with a B blood type tin can produce a child with either a B or an O blood type. This ofttimes led to inconclusive results, as 30% of the entire population can be excluded from being the possible parent under this form of testing.[eight] In the 1930s, serological testing, which tests certain proteins in the claret, became available, with a 40% exclusion rate.[9]
In the 1960s, highly accurate genetic paternity testing became a possibility when HLA typing was developed, which compares the genetic fingerprints on white blood cells betwixt the child and alleged parent.[10] HLA tests could be done with lxxx% accuracy only could non distinguish between close relatives.[11] Genetic parental testing technology advanced further with the isolation of the outset restriction enzyme in 1970. Highly accurate Deoxyribonucleic acid parental testing became available in the 1980s with the development of RFLP. In the 1990s, PCR became the standard method for Dna parental testing: a simpler, faster, and more accurate method of testing than RFLP, information technology has an exclusion rate of 99.99% or college.[11]
Legal evidence [edit]
The DNA parentage test that follows strict chain of custody can generate legally admissible results that are used for child back up, inheritance, social welfare benefits, immigration, or adoption purposes. To satisfy the concatenation-of-custody legal requirements, all tested parties have to be properly identified and their specimens collected by a third-political party professional who is not related to whatever of the tested parties and has no interest in the consequence of the test.
The breakthrough of bear witness needed is clear and convincing evidence: that is, more than evidence than an ordinary example in civil litigation, but less than beyond a reasonable doubt required to convict a accused in a criminal case.
In contempo years, clearing authorities in diverse countries, such as the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Commonwealth of australia, France, and others, may accept Dna parentage examination results from immigration petitioners and beneficiaries in a family unit-based immigration case when primary documents that prove biological relationship are missing or inadequate.
In the U.Due south., clearing applicants bear the responsibility of arranging and paying for DNA testing. The U.S. immigration authorities require that the DNA test, if pursued, be performed by one of the laboratories accredited by the AABB (formerly American Association of Blood Banks). Similarly, in Canada, the laboratory needs to be accredited by the Standards Council of Canada.
Although paternity tests are more common than maternity tests, at that place may exist circumstances in which the biological mother of the kid is unclear: examples include cases of an adopted child attempting to reunify with his or her biological female parent, potential hospital mix-ups, and in vitro fertilization where the laboratory may have implanted an unrelated embryo inside the mother.
Other factors, such as new laws regarding reproductive technologies using donated eggs and sperm and surrogate mothers, can also mean that the female giving nativity is not necessarily the legal mother of the child. For example, in Canada, the federal Human Assisted Reproduction Act provides for the use of hired surrogate mothers. The legal mother of the kid may be the egg donor. Similar laws are in place in the United Kingdom and Australia.
In Brazil in 2019, 2 male person identical twins were ordered to both pay maintenance for a kid fathered by one of them, because the father could non be identified with DNA.[12]
Legal bug [edit]
Australia [edit]
Peace-of-listen parentage tests are widely available on the internet. For a parentage test (paternity or maternity) to be admissible for legal purposes, such as for changing a nativity certificate, Family unit Police Court proceedings, visa/citizenship applications or kid support claims, the process must comply with the Family unit Law Regulations 1984 (Cth).[13] Farther, the laboratory processing the samples must be accredited by the National Association of Testing Authorities (NATA).[xiv]
Canada [edit]
Personal paternity-testing kits are available. The Standards Council of Canada regulates paternity testing in Canada whereby laboratories are ISO 17025-approved. In Canada, only a handful of labs take this approval, and information technology is recommended that testing is performed in these labs. Courts also have the power to order paternity tests during divorce cases.[15]
China [edit]
In China, paternity testing is legally available to fathers who suspect their child is not theirs. Chinese police force too requires a paternity test for any child born exterior the ane-child policy for the kid to be eligible for a hukou, or family registration record. Family tie formed by adoption tin can also only exist confirmed by a paternity test. A big number of Chinese citizens seek paternity testing each yr, and this has given rise to many unlicensed illegal testing centers being set.[xvi]
France [edit]
Deoxyribonucleic acid paternity testing is solely performed on conclusion of a approximate in case of a judiciary procedure in order either to constitute or contest paternity or to obtain or deny child support.[17] Individual DNA paternity testing is illegal, including through laboratories in other countries, and is punishable past up to a year in prison and a €15,000 fine.[eighteen] The French Quango of State has described the law'southward purpose as upholding the "French regime of filiation" and preserving "the peace of families."[19]
Frg [edit]
Under the Gene Diagnostics Deed of 2009, underground paternity testing is illegal. Any paternity testing must be conducted by a licensed dr. or by an expert with a academy degree in science and special education in parentage testing, and the laboratory carrying out genetic testing must be accredited according to ISO/IEC 17025. Total informed consent of both parents is required, and prenatal paternity testing is prohibited, with the exception of sexual abuse and rape cases. Whatever genetic testing done without the other parent's consent is punishable with a €5,000 fine.[twenty] Due to an amendment of the civil police force section 1598a in 2005, any human who contests paternity no longer automatically severs legal rights and obligations to the child.[21] [22]
State of israel [edit]
A paternity test with whatsoever legal standing must be ordered by a family court. Though parents take access to "peace of heed" parental tests through overseas laboratories, family unit courts are under no obligation to have them as bear witness. It is besides illegal to take genetic material for a parental exam from a minor over 16 years of historic period without the pocket-sized's consent. Family courts have the power to order paternity tests against the will of the father in divorce and child support cases, as well as in other cases such every bit determining heirs and settling the question involving the population registry. A human seeking to prove that he is not the father of the child registered equally his is entitled to a paternity test, even if the mother and natural guardian object. Paternity tests are not ordered when it is believed it could lead to the murder of the mother, and until 2007, were not ordered when there was a gamble that the kid could have been conceived exterior of marriage, making them a mamzer under Jewish law.[23] [24] [25]
Philippines [edit]
Dna paternity testing for personal knowledge is legal, and dwelling test kits are available by post from representatives of AABB- and ISO 17025-certified laboratories.[26] DNA Paternity Testing for official purposes, such equally sustento (child back up) and inheritance disputes, must follow the Dominion on Dna Testify A.M. No. 06-xi-5-SC, which was promulgated past the Philippine Supreme Court on Oct 15, 2007.[27] Tests are sometimes ordered by courts when proof of paternity is required.
Spain [edit]
In Spain, peace-of-mind paternity tests are a "big business," partly due to the French ban on paternity testing, with many genetic testing companies being based in Spain.[28] [29]
United kingdom [edit]
In the United Kingdom, at that place were no restrictions on paternity tests until the Homo Tissue Act 2004 came into strength in September 2006. Section 45 states that it is an offence to possess without appropriate consent any human bodily material with the intent of analysing its DNA. Legally declared fathers have access to paternity-testing services under the new regulations, provided the putative parental DNA being tested is their own. Tests are sometimes ordered by courts when proof of paternity is required. In the UK, the Ministry building of Justice accredits bodies that can conduct this testing. The Section of Health produced a voluntary lawmaking of practise on genetic paternity testing in 2001. This document is currently under review, and responsibility for it has been transferred to the Man Tissue Authorization. In the 2022 case of Anderson V Spencer the Court of Entreatment permitted for the very first time DNA samples taken from a Deceased person to be used for paternity testing.
United States [edit]
In the United states, paternity testing is fully legal, and fathers may test their children without the consent or knowledge of the female parent. Paternity testing have-abode kits are readily available for purchase, though their results are not admissible in courtroom and are for personal cognition only.
Only a court-ordered paternity exam may be used every bit evidence in court proceedings. If parental testing is beingness submitted for legal purposes, including immigration, testing must be ordered through a lab that has AABB accreditation for human relationship DNA testing.[30]
The legal implications of a parentage result examination vary by state and according to whether the putative parents are unmarried or married. If a parentage test does not meet forensic standards for the state in question, a court-ordered test may be required for the results of the test to be admissible for legal purposes. For unmarried parents, if a parent is currently receiving kid back up or custody, merely Deoxyribonucleic acid testing later proves that the man is not the father, support automatically stops. Nonetheless, in many states, this testing must be performed during a narrow window of fourth dimension, if a voluntary acknowledgement of parentage grade has already been signed by the putative begetter; otherwise, the results of the test may be disregarded by law, and in many cases, a man may exist required to pay child back up, though the child is biologically unrelated. In a few states, if the female parent is receiving the support, then that alleged father has the correct to file a lawsuit to go back any money that he lost from paying support. As of 2011, in most states, unwed parents confronted with a voluntary acknowledgement of parentage course are informed of the possibility and right to request a DNA paternity test. If testing is refused by the female parent, the father may not be required to sign the nativity document or the voluntary acknowledgement of parentage form for the child. For wedded putative parents, the husband of the mother is presumed to be the begetter of the child. But, in most states, this presumption tin exist overturned by the application of a forensic paternity examination; in many states, the fourth dimension for overturning this presumption may exist limited to the first few years of the child's life.
Contrary paternity testing [edit]
Reverse paternity determination is the ability to establish the biological male parent when the father of that person is not available. The test uses the STR alleles in the mother and her child, other children and brothers of the alleged father, and deduction of genetic constitution of the male parent past the basis of genetic laws, all to create a rough amalgamation. This can compare the father's DNA when a direct sample of the father'due south Deoxyribonucleic acid is unavailable. An episode of Solved shows this test being used to know if a blood sample matches with the victim of a kidnapping.
Run into besides [edit]
- Paternity fraud
- Mosaicism and chimerism, rare genetic weather condition that can result in fake negative results on DNA-based tests
- Non-paternity event
- Lauren Lake's Paternity Court, a television series that debuted in fall 2013
Genetic:
- Heritability
- List of Mendelian traits in humans
References [edit]
- ^ "A Non-invasive Test to Make up one's mind Paternity in Pregnancy" New England Journal of Medicine May iii, 2012
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (June nineteen, 2012). "Paternity Blood Tests That Work Early in a Pregnancy". The New York Times.
- ^ "Paternity Indices". April xix, 2004. Archived from the original on Apr 19, 2004.
- ^ "Two Women Don't Lucifer Their Kids' Deoxyribonucleic acid". Abcnews.go.com. August xv, 2006. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ Guo, Xin; Bayliss, Philip; Damewood, Marian; Varney, John; Ma, Emily; Vallecillo, Brett; Dhallan, Ravinder (2012). ""The New England Journal of Medicine "A Non-invasive Test to Make up one's mind Paternity in Pregnancy" May 3, 2012". New England Journal of Medicine. The New England Journal of Medicine. 366 (18): 1743–1745. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1113044. PMID 22551147.
- ^ "The New York Times "Before Nativity, Dad's I.D." June xx, 2012". The New York Times.
- ^ Gjertson, David W.; Brenner, Charles H.; Baur, Max P.; Carracedo, Angel; Guidet, Francois; Luque, Juan A.; Lessig, Rüdiger; Mayr, Wolfgang R.; Pascali, Vince L.; Prinz, Mechthild; Schneider, Peter M.; Morling, Niels (2007). "ISFG: Recommendations on biostatistics in paternity testing". Forensic Science International: Genetics. 1 (3–iv): 223–231. doi:x.1016/j.fsigen.2007.06.006. ISSN 1872-4973. PMID 19083766.
- ^ "History of DNA Testing - DNA Diagnostics Heart".
- ^ "History of DNA Testing - DNA Diagnostics Middle".
- ^ "The Tuscaloosa News - Google News Archive Search". news.google.com.
- ^ a b "Paternity Testing Resource". November 19, 2004. Archived from the original on November 19, 2004.
- ^ Cockburn, Harry (Apr 3, 2019). "Identical twins both ordered to pay child support after Dna tests fail to determine who babe's male parent is". The Independent . Retrieved April 4, 2019.
- ^ Court Ordered Paternity Tests - The Requirements of a Legal Paternity Test
- ^ National Association of Testing Authorities, Accredited Facilities
- ^ "Paternity Test - CanadianDivorceLaws.com". www.canadiandivorcelaws.com.
- ^ "Communist china'due south census gives ascension to paternity test, distrust; netizens' comments and our thoughts - Ministry of Tofu 豆腐部". www.ministryoftofu.com. Archived from the original on November 20, 2012. Retrieved Dec 20, 2012.
- ^ Art. 16-x of the Civil Code
- ^ Art. 226-25 to 226-30 of the Penal Code
- ^ "French men'southward insecurity over paternity of offspring creating 'a society of dubiousness'".
- ^ "BIONEWS - Germany passes genetic test laws". www.bionews.org.uk.
- ^ "Alpha Biolabs - Paternity Test". November 19, 2010. Archived from the original on November 19, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Constitutional Court Rules Secret Paternity Tests Still Illegal - Germany- News and in-depth reporting from Berlin and beyond - DW - 13.02.2007". DW.COM.
- ^ "Courtroom Orders Paternity Test Despite 'Mamzer' Factor - Israel National News". Israel National News.
- ^ Sinai, Ruth (October 22, 2008). "Court May Side With Husband on Paternity Test". Haaretz.
- ^ Ilan, Shahar (July 24, 2008). "MKs Okay Paternity Testing". Haaretz.
- ^ "Fast, 100% Accurate AABB DNA Paternity Test - Philippines". dnahustisya.ph.
- ^ Dna Rules of Testify: Philippines Archived 2014-01-20 at annal.today
- ^ "AFP: Paternity tests take off in Kingdom of spain thanks to French ban". Feb 10, 2013. Archived from the original on February 10, 2013.
- ^ "Espana Offers Paternity Tests to Suspicious French Fathers". Medindia. Nov 28, 2007.
- ^ "Accredited Parentage Testing Facilities". Feb 18, 2006. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
External links [edit]
- UK paternity testing regulations per the Human Tissue Authority
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_paternity_testing
0 Response to "Can a Paternity Test Distinguish Between Father and Son"
Post a Comment